Home
STM32F411 Black Pill
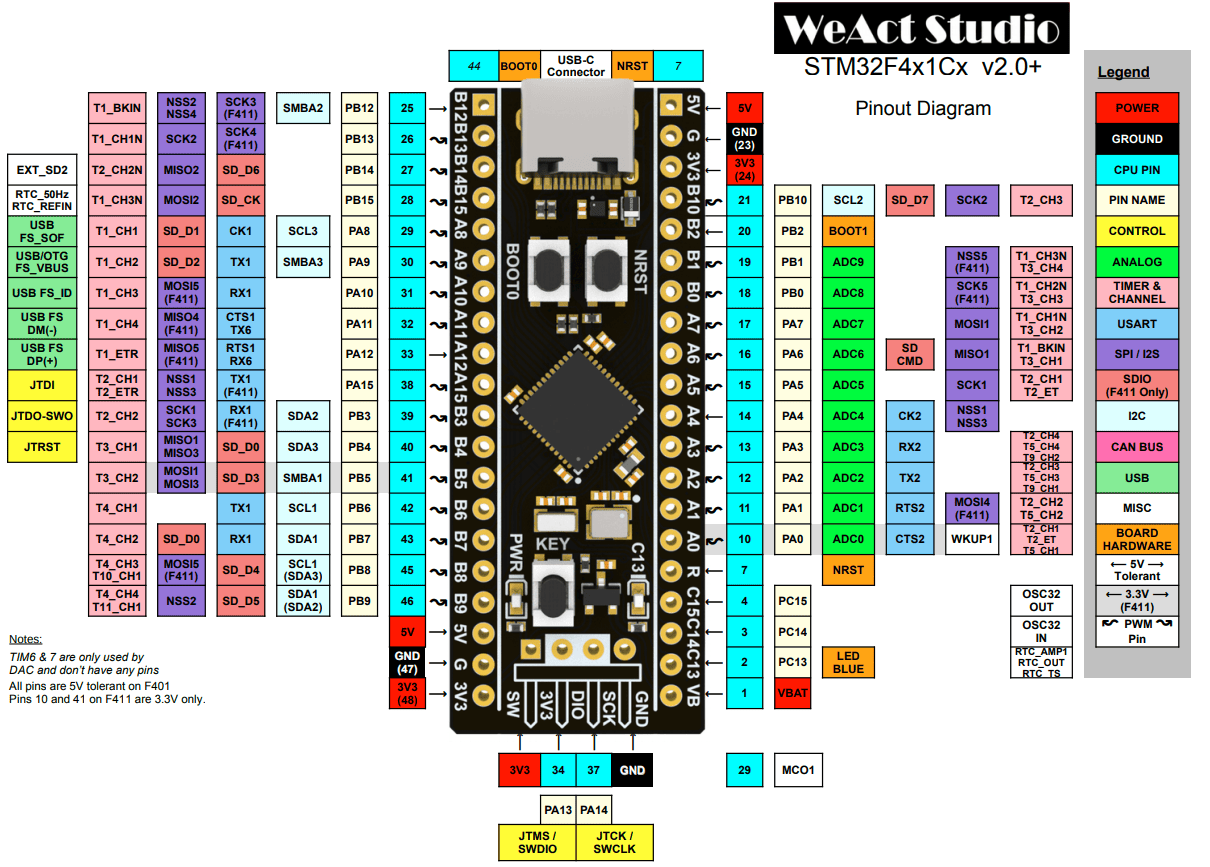
| Feature |
Specs |
| CPU |
Cortex-M4 100MHz |
| RAM |
128kB |
| Flash |
512kB |
| GPIO |
32 |
| ADC |
12 bit |
| USB |
1.1 Host/Device |
| UART |
3 |
| I2C |
3 |
| SPI |
5 |
| I2S |
2 |
| Current consumption |
26mA |
GPIO allows the software to turn on and off a pin and read high or low from a pin.
- CubeMX: GPIO_Output or GPIO_Input
- HAL
void HAL_GPIO_WritePin(port, pin, pinState)void HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(port, pin)PinState HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(port, pin)
- Arguments
- port:
GPIOA, GPIOB, GPIOC
- pin:
GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_2, …
- pinState:
GPIO_PIN_SET, GPIO_PIN_RESET
PWM approzimates an analog voltage by quickly switching between a fixed high voltage and ground so the average over time is the desired analogy voltage.
- PWM has three variables
- Duty cycle - Percentage of time the pin is on during the cycle.
- Resolution - Number of possible duty cycle values.
- Frequency - How many times the cycle repeats per second.
Microcontrollers use a timer that counts up to a set value, then resets to 0. This is one PWM cycle, consisting of a high phase and a low phase. When the timer count exceeds a compare vlaue, the output switches from high to low. Changing this compare value changes the duty cycle. Chaning the maximum count value changes the resolution. The frequency depends on the clock frequency and the resoltion, where high resoltion lowers the frequency.
Ex: Given a system clock cycle of 72MHz and 8-bit(0-255) resolution, what’s teh frequency of the PWM?
$\frac{72,000,000 \text{ counts}}{1 \text{ sec}} * \frac{1 \text{ cycle}}{256 \text{ counts}} = 218,250 \text{ cycles per second}$
- CubeMX
- Click Timers on the left
- Select any general purpose timers: TIM2, TIM3, etc.
- Clock Source: Internal Clock
- Channel#: PWM Generation CH#
- The channel changes which pin the PWM is outputed on.
- Under Configuration, Parameter Settings
- Counter Period: Max number the timer counts up to.
- Pulse: The compare value to set the duty cycle. Has to be less than the counter period.
- HAL
HAL_TIM_PWM_Start(htimPtr, channel);__HAL_TIM_SET_COMPARE(htimPtr, channel, pulse); - Changes the duty cycle.
- Arguments
- htimPtr: Reference to the timer.
&htim1, &htim2, …
- channel:
TIM_CHANNEL_1, TIM_CHANNEL_2, …
- pulse: 0 to counter period.
- Advanced settings
- Prescaler: The timer only increments after it has counted to the prescalar, it’s used to slow down the timer.
- CubeMX
- Under Connectivity: USART#
- Mode: Asynchronous
- Set Baud Rate
- HAL
HAL_UART_Transmit(uart, bufferArr, size, timeout);HAL_UART_Receive(uart, bufferArr, size, timeout);
- Arguments
- uart:
&huart1, &huart2, etc.
- bufferArr is an array of uint8_t
- size is the number of bytes to transmit or receive(uint16_t).
sizeof(bufferArr) - 1
- timeout in milliseconds
- CubeMX
- Under Connectivity: I2C#
- Set Primary slave address: Is your device’s slave address if it’s used as an I2C slave.
- HAL
HAL_I2C_Master_Transmit(hi2c, address, bufferArr, size, timeout);HAL_I2C_Master_Receive(hi2c, address, bufferArr, size, timeout);HAL_I2C_Slave_Transmit(hi2c, bufferArr, size, timeout);HAL_I2C_Slave_Receive(hi2c, bufferArr, size, timeout);
- Arguments
- hi2c:
&hi2c1, &hi2c2, etc.
- address is the address left shifted by 1.
0x3C << 1
- bufferArr is an array of uint8_t
- size is the number of bytes to transmit or receive(uint16_t).
- timeout in milliseconds
- Timers
- RTC - Low power real time clock.
- TIM1 - Advanced control timer.
- For precise PWM and motor control.
- TIM2 and TIM5 - 32 bit general purpose timers.
- TIM3 and TIM4 - 16 bit general purpose timers.
- TIM9, TIM10, and TIM11 - 16 bit general purpose timers.
- Each timer controlls certain pins(~4).
- The channel sets which particular pin.
-
-
Trigger Output (TRGO) Parameters - When you want one timer to trigger another timer.
HAL_Delay(ms)-
millis(), micros()
-
A watchdog timer - A timer that needs to be periodically refreshed within a time interval, otherwise it resets the device because it indivates the code is no longer runnign corrently.
- Timer
- HAL_Delay(uint32_t ms);
- HAL_TIM_Base_Init(TIM_HandleTypeDef *htim)
- HAL_TIM_Base_Start(TIM_HandleTypeDef *htim)
- HAL_TIM_Base_Stop(TIM_HandleTypeDef *htim)
- Power modes
- HAL_PWR_EnterSleepMode(Regulator, SLEEPEntry);
- HAL_PWR_EnterStopMode(Regulator, STOPEntry);
- HAL_PWR_EnterStandbyMode();
- Watchdog
- HAL_IWDG_Init(IWDG_HandleTypeDef *hiwdg)
- HAL_IWDG_Start(IWDG_HandleTypeDef *hiwdg)
- HAL_IWDG_Refresh(IWDG_HandleTypeDef *hiwdg) - Resets the watchdog timer to prevent a reset.
TIM2_IRQHandler - is a special function name that matches the entry in the STM32 interrupt vector table for TIM2.
- So when TIM2 throws an interupt event, this function is automatically called.
HAL_TIM_PWM_Start_IT(htim, Channel);
- Starts the interupts associated with the timer.
- Need to Enable NVIC Settings: TIM# global interupt
Direct memory access.
- Allows a pin to directly set addresses.
#include "core_cm4.h"
void ITM_Print(char *s) {
while (*s) {
ITM_SendChar(*s++);
}
}
// usage
ITM_Print("Hello SWO\n");
- Install: CubeMX and STM32CubeIDE for Visual Studio Code(stmicroelectronics.stm32-vscode-extension).
- Generate starter code for CubeMX
- File -> New Project
- Type in your Commercial part number: STM32F411CEU6
- Start project in the top right
- Pinout & Configuration
- Project manager
- Project Name
- Project Location
- Toolchain/IDE: CMake
- GENERATE CODE in the top right
- Wire ST-Link
| ST-Link Pin |
Board Pin |
| GND |
GND |
| 3.3v |
3.3v |
| SWDIO |
DIO |
| SWCLK |
SCLK |
- If it’s your first time using your ST-Link device, you’ll need to upgrade its firmware.
- Left side in vs code click Run and Debug icon
- Under STM32CUBE DEVICES AND BOARDS at the bottom left
- Click the little download icon
- Setup your code
- Create My_Code folder at the root level of your project.
In my_main.h
#include "stm32f4xx_hal.h"
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
void myCode();
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
In my_main.cpp
#include "my_main.h"
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
void myCode(){
// Init code
while(true) {
// Loop code
}
}
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
- In Core/Src/main.c
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
#include "../../My_Code/my_main.h"
/* USER CODE END Includes */
// ...
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
myCode();
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
- In CMakeLists.txt
file(GLOB MY_CODE_SOURCES My_Code/*.cpp)
target_sources(${CMAKE_PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE
# Add user sources here
${MY_CODE_SOURCES}
)
- Compiling, Flashing, and Debugging
- Top bar -> Run -> Start Debugging or Run Without Debugging
- If it’s your first time, you’ll have to accept the popups that show up in the bottom right.
- If you add new .cpp files, you may have to delete build/ to ensure CMake adds it in.
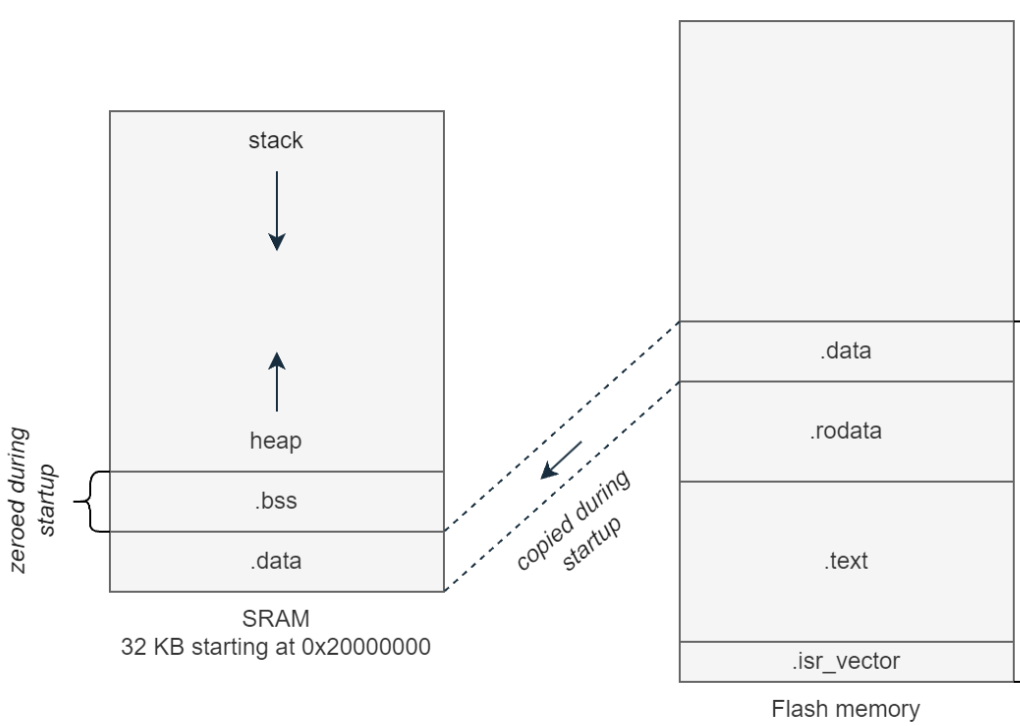
- Flash - Slow, permanant storage.
- SRAM - Fast, reset after power off.
| Memory |
Description |
| .isr_vector |
Stores interrupt vectors and reset handler addresses. |
| .text |
Your code |
| .rodata |
Read only constants and literals. |
| .data |
Initialized global and static variables. |
| .bss |
Uninitialized global and static variables. |
- Interrupt vectors - Pointer to functions that run when an interrupt happens.
- Reset handler - The function that is ran first after a reset to initialize the system before main().
- .data is copied from flash to sram
- .bss is zeroed
- CMSIS - Collection of components for Arm Cortex-based microcontrollers.
- API to the core registers.
- DSP library - Optimized signal processing functions.
- RTOS abstraction layer
- DMA controller code - Transfers data between memory and peripherals without involvement of the CPU.


